Hi! This blog is no longer updated, but on this page you can find an archive of my blog posts, 2016-2022. Click here to view the blog index (a list of all posts).
For the latest news about Step Up Japanese, sign up to my newsletter.
Search this blog:
Why Does Everybody Forget Katakana?
I'll let you into a secret. I used to hate katakana.
Students of Japanese tend to start with its two phonetic alphabets. We start with hiragana, the loopy, flowing letters that make up all the sounds of Japanese.
Then we move on to katakana - all the same sounds, but in angular blocky font.
Hiragana seems fairly straightforward, I think. And when you start learning Japanese everything you read is written in hiragana, so by reading you constantly reinforce and remember.
Katakana? Not so much.
I'll let you into a secret. I used to hate katakana.
Students of Japanese tend to start with its two phonetic alphabets. We start with hiragana, the loopy, flowing letters that make up all the sounds of Japanese.
Then we move on to katakana - all the same sounds, but in angular blocky font.
Hiragana seems fairly straightforward, I think. And when you start learning Japanese everything you read is written in hiragana, so by reading you constantly reinforce and remember.
Katakana? Not so much.
The katakana "alphabet" is used extensively on signs in Japan - if you're looking for カラオケ (karaoke) or ラーメン (ramen noodles) you'll need katakana.
But if you're outside Japan, then beyond the letters in foreign names, you probably don't get a lot of exposure to katakana.
I think that's why a lot of beginning students really struggle to remember katakana.
Here are a couple of suggestions:
1) Use mnemonics
I learned katakana using mnemonics. For example, I still think katakana ウ (u) and ワ (wa) look super similar - I remember that ウ has a dash on the top, just like hiragana う (u) .
2) Practice, practice, practice
I'm not a huge fan of having you simply copy letters over and over again, but there is something to be said for "writing things out". By writing letters down, you activate muscle memory, which helps you remember. So get writing katakana!
3) Start learning kanji
It might feel like running before you can walk, but starting to read and write kanji (Chinese characters) before your katakana is completely perfect can be a good option.
Kanji textbooks have the Chinese readings of the characters in katakana, so learning kanji is also really good katakana practice.
And maybe, just maybe, you'll turn into a katakana lover?
Updated 23rd Oct 2020
How to Learn Hiragana and Katakana using Mnemonics
I finally got around to going through the mid-course feedback from my students and drawing up plans to incorporate some of what you asked for into the rest of the course. Several learners mentioned the importance of learning the kana early on.
Learning to read Japanese can be a daunting task. The Japanese language has three distinct "alphabets" (four if you count romaji!) and learning kanji is a task that takes years. You can learn the kana (hiragana and katakana) pretty quickly, though, if you use the most efficient way to memorise them - mnemonics.
Hi! This article was first published in April 2017. I updated it recently (April 2020) and fixed some broken links.
This week I finally got around to going through the mid-course feedback from my students and drawing up plans to incorporate some of what you asked for into the rest of the course.
Several learners mentioned the importance of learning the kana early on.
Learning to read Japanese can be a daunting task. The Japanese language has three distinct "alphabets" (four if you count romaji!) and learning kanji is a task that takes years.
You can learn the kana (hiragana and katakana) pretty quickly, though, if you use the most efficient way to memorise them - mnemonics.
Hiragana and Katakana are the "building blocks" of the Japanese written language. Students in my beginner Japanese classes mostly start with the romaji edition of 'Japanese For Busy People'*, because my priority is to get you speaking from day one, and to spend class time on speaking as much as possible. Reading and writing is mostly set as homework.
But if you want to learn to read Japanese, you definitely need to start by learning hiragana - the 46 characters that make up the first basic Japanese “alphabet”. But how to remember them?
The best, quickest, most fun method is to associate each character with a picture that it (clearly or vaguely) looks like, ideally also using the sound of the letter.
Hiragana and katakana are pretty simple, so associating each character with a picture is super easy.
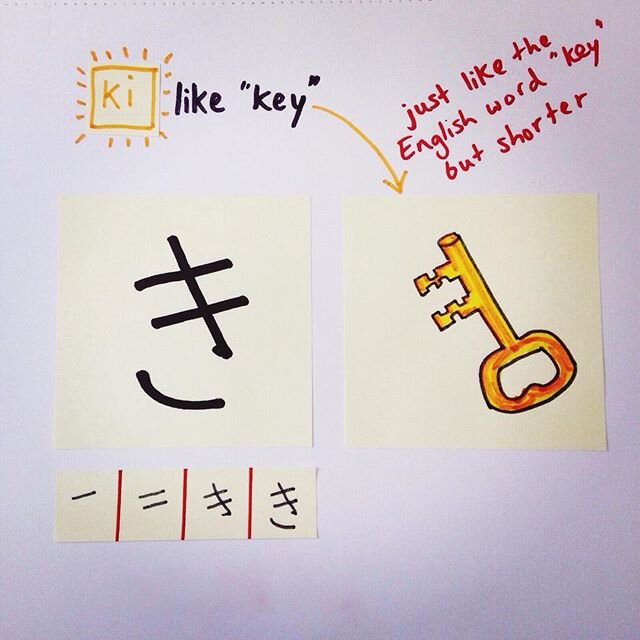
Here's hiragana き (ki), which we can imagine is a picture of a KEY. My image of akey is an old-fashioned one. Yours might be modern and spiky. Or it might have wings on it and be flying about getting chased by Harry Potter on a broomstick.
The point is to think of a strong visual image that makes the picture of the key stick in your mind:
Of course, you need to learn to read words and sentences too. So as well as learning each letter, you need to practice writing and reading. This where the mnemonic really sinks in.
Memorisation doesn't help you remember. What helps you remember is active recall.
Let me give you an example.
You're reading a sentence and come across the word きのこ (kinoko, mushroom). You're staring at the letter き - "which one was that again?" and struggle a little bit to remember it.
Then you remember - aha! it's the KEY! This is ki.
This process of active recall - pushing a little bit to remember something - is the process that cements the mnemonic in your mind.
For me, one of the great thing about using mnemonics to remember the kana is that when I explain the system to learners, they often tell me that's what they're doing anyway, even if they don't have a name for what they're doing:
"Oh yes, that's how I remember む too - it's a funny cow's face! MOO"
"No, む is a man saying MO-ve!"
I've also found - luckily for me - it doesn't matter seem to matter if the actual picture is rubbish. (You don't even have to draw them, I just did this to help my students out and to share the idea).
What's important is that the picture in your head is super clear.
...and once you finish hiragana, you can do the whole thing again for katakana (the second basic Japanese alphabet):
You can find the whole set of hiragana and katakana mnemonics on instagram with the hashtag #stepupkana - please check it out and let me know what you think.
I'd love to hear what mnemonics you use to help remember the kana - let me know in the comments or add your story to the instagram posts for that character.
*Links with an asterisk * are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission, at no extra cost to you, when you click through and buy the book. Thanks for your support!
First published April 2017
Updated 7th April 2020
Why Does The Japanese Language Have So Many Alphabets?
My students ask a lot of good questions. And one that sent us off on a bit of a tangent a few weeks ago was: “how old is Japanese writing?”
So, let’s take a whistle-stop tour of Japanese history with a very brief introduction to the Japanese writing system!
My students ask a lot of good questions. And one that sent us off on a bit of a tangent a few weeks ago was: “how old is Japanese writing?”
So, let’s take a whistle-stop tour of Japanese history with a very brief introduction to the Japanese writing system!
Until the 1st or 2nd century, Japan had no writing system. Then, sometime before 500AD, kanji - Chinese characters - made its way to Japan from China (probably via Korea).
These characters were originally used for their meaning only - they weren't used to write native Japanese words.
↓ And at that time, Japanese writing looked like this. Look, it looks like Chinese!

(Image Source - Nihon Shoki, Wikipedia)
But it was inconvenient not being able to write native Japanese words down, and so people began to use kanji to represent the phonetic sounds of Japanese words, not only the meaning. This is called manyougana and is the oldest native Japanese writing system.
For example, in manyougana the word asa (morning) was written 安佐 (that's a kanji for the “a” sound - 安 - and another for the “sa” sound - 佐). These characters indicate the sound of the word - “asa” - but not its meaning.
In modern Japanese we'd use 朝, the kanji that means "morning" for asa. This character shows its meaning AND its sound.
The problem was, manyougana used multiple kanji for each phonetic sound - over 900 characters for the 90 phonetic sounds in Japanese - so it was inefficient and time-consuming.
Gradually, people began to simplify kanji characters into simpler characters - that's where hiragana and katakana came from.
Katakana means "broken kana" or "fragmented characters". It was developed by monks in the 9th century who were annotating Chinese texts so that Japanese people could read them. So katakana was really an early form of shorthand.
Each katakana character comes from part of a kanji: for example, the top half of the kanji 呂 became katakana ロ (ro), and the left side of the kanji 加 became katakana カ (ka).
↓ Each katakana comes from part of a kanji.

(Source - Katakana origins, Wikipedia)
Women in Japan, on the other hand, wrote in cursive script, which was gradually simplified into hiragana. That's why hiragana looks all loopy and squiggly. Like katakana, hiragana characters don't have meaning - they just indicate sound.
↓ How kanji (top) evolved into manyougana (middle in red), and then hiragana (bottom).

(Source - Hiragana evolution, Wikipedia)
Because it was simpler than kanji, hiragana was accessible for women who didn't have the same education level as men. The 11th-century classic The Tale of Genji was written almost entirely in hiragana, because it was written by a female author for a female audience.
Modern Japanese writing uses all three of these “alphabets” - hiragana, katakana, and kanji - often all mixed up in the same sentence.
What would 12th-century people in Japan think of my students, 900 years later, learning hiragana as they take their first steps into the Japanese language?
First published 28th Oct 2016
Updated 27th Jan 2020
Is it Shinbun or Shimbun?
It’s both. And it’s neither.
Beginner students often ask whether “shinbun” or “shimbun” (the word for “newspaper” in Japanese) is correct.
You’ll see both spellings...and books about the Japanese language don’t seem to be able to agree either.
If you look at the two most popular Japanese beginner textbooks, Genki has “shinbun”, whereas Japanese for Busy People has “shimbun” and also “kombanwa”.
But why?
It’s both. And it’s neither.
Beginner students often ask whether “shinbun” or “shimbun” is the correct spelling of the word for “newspaper” in Japanese.
You’ll see both spellings… and books about the Japanese language don’t seem to be able to agree either.
If you look at the two most popular Japanese beginner textbooks, Genki has “shinbun”, whereas Japanese for Busy People has “shimbun” and also “kombanwa”.
But why?
Well, there are different ways of writing Japanese in romaji (roman letters i.e. the alphabet). All romaji is an approximation, and there are two different major systems, both used widely.
In elementary school, Japanese kids learn Kunrei, the government’s official romanization system. Kunrei is more consistent, but not particularly intuitive for non-Japanese speakers.
In the Kunrei system:
しょ is written as “syo”
こうこう is written as “kookoo”
But textbooks for people learning Japanese tend to use the Hepburn system, which is easier for non-native speakers. Modernised Hepburn writes しょ as “sho” and こうこう as “kōkō”.
"N or M?"
Under the older Hepburn system of romaji, a ん (n) before a "b" or "p" sound used to be written as m. This gave us romaji spellings like shimbun and sempai. (The Kunrei system, on the other hand, never used this rogue "m" at all).
When Modernised Hepburn was introduced in 1954, the "m" rule was dropped. Since 1954, both major systems have said that these words should be written as shinbun and senpai.
So shimbun-with-an-m hasn't been officially used since 1954...but it is still the preferred romanization of several major Japanese newspapers: Asahi Shimbun, Yomiuri Shimbun, Mainichi Shimbun.
So it seems like shimbun-with-an-m is still with us.
"So which is better?"
Arguably, “shimbun” is closer to the pronunciation of the word. There IS a sound change going on here – before a “p” or “b” sound in Japanese, the ん sounds more like “m” than “n”.
But "shinbun" is more consistent, and personally I prefer it - especially if you’re still learning kana.
There is no ‘m’ hiragana, and I don’t want you wasting your time looking for it on your kana chart.
"Which is more common?"
I don’t know. But it kind of doesn’t matter which one is more common: the Japanese way to write the word for newspaper isn't “shinbun” or “shimbun”. It’s not really even しんぶん. The Japanese word for newspaper is 新聞.
Which brings me neatly onto my next question...
“Why are you writing it in romaji anyway?"
Some people say that the shimbun/shinbun thing is a slightly pointless question. Everyone should just learn the kana, and then we wouldn't have this problem, right?
But romaji isn’t just read by people learning Japanese. Romanised stations and place names and even people's names are read by millions of people visiting Japan who don’t know Japanese.
And for people who don’t speak Japanese (especially English speakers), it's easier to guess the pronunciation of “shokuji” than “syokuzi”.
So, while the current system is a bit of a muddle, it's the best thing we've got. I think we can all agree on that.
(First published February 12, 2016. Updated June 21, 2019)
How to Use Anki to Not Forget Vocabulary
Lots of you probably use flashcards already. Why not use really, really clever ones?
Imagine you're studying Japanese vocabulary with a set of flashcards. You go through the cards one by one, putting them into a "pass" pile if you remembered them, and a "fail" pile if you didn't.
When you finish, you work through the "fail" pile again. You get about half of them right.
The next day, you go through all the cards again. It takes ages, and it's boring - you did all these yesterday…
You want to use flashcards. Why not use really, really clever ones?
Imagine you're studying Japanese vocabulary with a set of paper flashcards. You go through the cards one by one, putting them into a "pass" pile if you remembered them, and a "fail" pile if you didn't.
When you finish, you work through the "fail" pile again. You get about half of them right.
The next day, you go through all the cards again. It takes ages, and it's boring - you did all these yesterday.
Or maybe you start with the "fail" pile. But this card pile is smaller, so when the cards come up, you just remember the fact that you failed them yesterday!
This approach is okay, if you’re enjoying yourself. (Anything is okay, as long as you're having fun. This is my basic approach to language learning).
But you can make flashcards much more efficient - and stop wasting your time - with a spaced repetition system like Anki.
The power of active recall
When you use flashcards to test yourself, you're engaging in active recall - you're pushing your brain to remember something. This is the most effective way to commit things to memory.
You know that feeling when you're struggling to remember a word, and then finally get to it? That's active recall.
At that moment, you've just cemented the correct meaning of the word in your mind. And you'll remember it much quicker next time.
What is Anki?
Anki is a spaced repetition system (SRS) - a system for remembering things. It's free for PC / Mac, and Android. The iPhone app is not free (it’s £23.99), so I'd try it out on a computer first and see if you like it.
(Then again, it might be the best £23.99 you ever spend...)

Anki shows you digital flashcards and tests you. It then spaces out the cards into the future, depending on how difficult you found them.
If you don't remember a word, Anki shows you it again in 10 minutes.
If you said it's easy, it might show you in three days. If in three days it's still easy, it waits seven days before it tests you on that word again.
If you keep getting it right, the interval increases exponentially, until Anki knows it'll be years before you forget that word. When you get it wrong, Anki knows you need to practice that word again soon.
So Anki sorts the “piles” of flashcards for you, testing you on material just as it thinks you're about to forget it.
I told you it was clever.
What to study?
Anki has shared decks that you can download - sets of flashcards made by other users.
If you're studying for the JLPT, there are loads of decks for that. And whatever Japanese textbook you're using, there'll be an Anki deck for it.
You probably don’t want to memorise every word in your textbook - maybe you don't think you need the word for "municipal hospital", or you want to focus on certain areas. Just delete the cards you don't need.
Or you can make your own decks by adding your own material. That's probably the best approach.
Maybe you want to memorise verb conjugations (masu form to -te form; -nai form, etc). Or maybe you just can't remember the difference between ウ and ワ. Stick it in your Anki deck, and forget about forgetting things.

What not to study
A word of caution - don't try and memorise things you don't understand yet.
For example, let's say in your textbook there's a chart giving the -nai forms of common verbs. You could put those in your anki deck and memorise them, I guess.
But it's no use if you don't know what the -nai form is and how it's used. Learn what it is - practice it, speak it, own it - and use spaced repetition to help you remember.
A useful companion
I tried to use Anki to re-learn some French last year (my high school French class was a long time ago).
I downloaded a beginner French deck, and I'd sit on the train testing myself on vocabulary. It helped a bit, but I didn't magically learn to speak French! That's basically because I never tried to produce any French in that time. I didn't speak with anyone or write down anything in French...
To master a language, you need to speak out loud, and listen a lot.Spaced repetition is a brilliant tool and a companion to learning. But it's not everything... you need to actually practice too.
I'd love to know how you're getting on with Anki. Do you love it or hate it? Tweet me a screenshot of your cards, or let me know in the comments.
First published May 08, 2017
Updated October 09, 2018