Hi! This blog is no longer updated, but on this page you can find an archive of my blog posts, 2016-2022. Click here to view the blog index (a list of all posts).
For the latest news about Step Up Japanese, sign up to my newsletter.
Search this blog:
Dr. Anki or, How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Embrace Multiple Decks (GUEST POST!)
A special guest post from Step Up Japanese student Phil Kinchington!
Anki is a flashcard app that uses a Spaced Repetition System (SRS) to help you learn and memorise information by creating strong, long-lasting memories. It does this by aiming to present you with a flashcard exactly at the point you were about to forget it.
You should be able to recall the information, but at a slight stretch. If you remember the card correctly, it will increase the length of time before it shows it to you again. If you can’t remember (or remember incorrectly) it will show it to you again sooner. It was originally developed for language learning (being named after the Japanese word for ‘memorisation’) but has since been applied to many subjects, including medical studies…
A special guest post from Step Up Japanese student Phil Kinchington!
Anki is a flashcard app that uses a Spaced Repetition System (SRS) to help you learn and memorise information by creating strong, long-lasting memories. It does this by aiming to present you with a flashcard exactly at the point you were about to forget it.
You should be able to recall the information, but at a slight stretch. If you remember the card correctly, it will increase the length of time before it shows it to you again. If you can’t remember (or remember incorrectly) it will show it to you again sooner. It was originally developed for language learning (being named after the Japanese word for ‘memorisation’) but has since been applied to many subjects, including medical studies.
While I saw Anki mentioned and recommended everywhere, I could never figure out a way to use it that really worked for me. Some people recommended that you should download a pre-made deck to match the textbook you are using (there is a huge library of decks submitted by users accessible from within Anki.) But I felt this would mean that it would start automatically adding vocabulary past the point I’d got to in the book.
(Note from Fran - you can “suspend” all the cards and manually “unsuspend” them as you work your way through a textbook, although I appreciate this is a bit fiddly!)
A lot of people recommended that you should use a single deck, and dump everything you came across into it, which seems a bit too messy for my liking. Also, I'd then be constantly having the dilemma of "do I put this in, or is it not worth it, or how can I add this in a meaningful way, that I'd understand why it was there when I came back to it?"
A big part of the problem is how open and flexible the system is. Anki doesn’t guide you or force you to work with it in a specific way, and the design of the cards is almost infinitely configurable. Of course, this is also the reason it has been possible to adapt it for so many different subjects.
I’d pretty much given up trying, and then I discovered the Alivia’s Japanese Nook YouTube channel. On that channel Alivia has a video specifically about using Anki to study Japanese that has been very useful to me. It's a bit long, as it covers every detail of how to use it, and exactly how she has all the settings configured. But if you’ve never used Anki at all, it’s a very good guide to getting it set up and starting to use it.
As a result of watching this video, I have developed a way of using Anki that seems to be working for me. I have multiple decks. Firstly I have a 'Genki' deck, which I'm manually populating with the vocabulary from the vocab pages in each chapter. This way, I can control how far ahead it goes. The other deck is the one recommended in this video called 'JLPT Tango N5 MIA Japanese' (it is a deck that has been built to go along with the JLPT Tango N5 study book*.) Over a month later and it still seems to be working for me, which is better than I've ever managed with it - every time I've tried, I've bounced off pretty hard and pretty fast.
The JLPT deck mostly uses the vocabulary in phrases, which is more useful for remembering and understanding the usage (although, I've just been through a batch where it felt it was essential to go through every month of the year, and also a whole load of one person, two people, three people, six people, etc.)
It also uses kanji from the start, and you don't get the furigana until you click through to the answer, which could be a bit harsh depending on how many kanji you‘ve already been exposed to. But so far they've all been pretty common kanji that I was already comfortable with. Each card also has full voice recordings that automatically play when you click to show the answer. Sometimes several versions with different voices.
So now my method is: look at the card, read the phrase aloud, then say aloud "that means" followed by saying my translation aloud. When I click through to the answer, depending on whether I've got it right or not I'll click either 'Good' or ‘Again’. I don't use the ‘Easy’ or 'Hard' options at all. As far as I'm concerned it was either Good/Satisfactory or Again/Wrong.
I give myself a bit more leeway on the translation of, for example, words like 'international/foreign student' or 'nice/pleased to meet you, how do you do, etc.' But when it comes to the Japanese, I try to be pretty hard on myself regarding kanji recognition, pronunciation, etc. Better to practice something a little more than you needed to, rather than less than you required.
Now that I’ve found that there’s no need to worry about getting overwhelmed by having multiple decks, I’m thinking of adding more. First candidate is all of the sentences from the first book or two in the Unko Sensei series. This will have the advantage that it will force me to develop my own English translations, adding an extra layer of study.
How do you study Japanese with Anki? How are your decks set up? Let us know in the comments!
Links with an asterisk* are affiliate links, which means I (Fran) may earn a small commission, at no extra cost to you, when you click through and buy the book. Thanks for your support!
Click here for more guest posts from Step Up Japanese students!
"How Did You Learn Kanji?"
I had a friend in 2011 who also lived in Japan and was also learning Japanese. Like me, he hoped to be fluent one day. I told him that I was going to learn all 2136 common-use kanji by making up a mnemonic story for each one. He laughed at me, of course. I don’t blame him.
But this slightly convoluted method is the thing that took my Japanese kanji knowledge from beginner to advanced.
So here is the story of how I studied kanji, some suggestions for kanji practice, plus some advice from another friend who took a totally different approach to me. I hope you’ll find it useful!
I had a friend in 2011 who also lived in Japan and was also learning Japanese. Like me, he hoped to be fluent one day. I told him that I was going to learn all 2136 common-use kanji by making up a mnemonic story for each one. He laughed at me, of course. I don’t blame him.
But this slightly convoluted method is the thing that took my Japanese kanji knowledge from beginner to advanced.
So here is the story of how I studied kanji, some suggestions for kanji practice, plus some advice from another friend who took a totally different approach to me. I hope you’ll find it useful!
Learning kanji takes time
Written Japanese uses a mix of three “alphabets” - hiragana, katakana, and kanji (Chinese characters).
Individual hiragana and katakana characters indicate sound only - the hiragana character あ makes the sound “a”, but it doesn’t have any meaning by itself. (Just like how the letter “B” doesn’t have any meaning by itself - it’s just a sound).
Kanji, on the other hand, indicate meaning as well as sound. For example, the kanji 木 means “tree”; 重 means “heavy”.
To read Japanese fluently, a student must be able to understand at least 2000 kanji. There is even an official list of the 2136 kanji that all Japanese children learn by the end of secondary school, called the jōyō kanji (常用漢字, meaning “regular-use kanji”).
The task of learning at least 2000 kanji is a major undertaking - even for Japanese people. That’s why students in Japan continue learning the jōyō kanji right up until the end of high school. And traditional methods of learning kanji tend to focus on rote memorisation, which is very inefficient.
The Heisig Method
When I got serious about learning kanji, in 2010, I did a bit of googling and stumbled across people talking about “the Heisig method”. This is the kanji study method introduced by James W. Heisig in his popular (and somewhat controversial) book ‘Remembering the Kanji I: A complete course on how not to forget the meaning and writing of Japanese characters’.*
The Heisig approach can be summed up as follows:
1) Learn the meaning of kanji
2) Learn the meaning of radicals
3) Memorise how to write kanji by making up descriptive mnemonic stories
You’ll note that reading kanji (how to pronounce them) does not feature on this list.
1) Learn the meaning of kanji
Heisig argues that before learning the readings of any kanji characters, it is more efficient to first learn the meanings. To this end, he gives each kanji an English keyword. For example, the kanji character 行 means “go”, so Heisig gives it the English keyword “going”.
By learning the meanings of kanji, the learner can guess at unfamiliar words.
I got to show off this ability years later in Okinawa, when my good friend Karli and I were looking at some artefact:
“What’s it made of?” she asked.
“I think it’s ivory.”
“Fran, why the hell do you know the Japanese word for ‘ivory’?”
“I don’t,” I said, pointing at the sign which had the word 象牙 on it. “But this one (象) "means ‘elephant’, and this one (牙) means ‘tusk’.”
2) Learn radicals
Heisig also puts a lot of focus on learning radicals - small parts which make up kanji. (He calls them “primitive elements”, but radicals is a more commonly-used term).
Radicals are the building blocks of kanji, and by learning to identify these constituent parts, you can “unpick” new and unfamiliar characters. Knowledge of radicals is also very helpful for looking up kanji in a dictionary.
For example, the kanji 明 (meaning “bright”) is made up of the two smaller parts 日 (“sun“) and 月 (“moon”). If the SUN and the MOON appeared in the sky together, that’d be pretty BRIGHT, right?
3) Make mnemonics
Using these radicals, Heisig argues that by making vivid and memorable stories, you can remember even complex kanji easily.
A common and simple example of a kanji mnemonic is 男, the character for “man”. The top half of this kanji is 田 “rice field“, and the bottom half is 力, “power”. So here’s the image: A MAN is someone who uses POWER in the RICE FIELD.
(If you’re not great at making up mnemonics, you can do what I did and copy other people’s funny stories from the Kanji Koohii website).
4) Practice writing by hand - from memory
Heisig says that in order to learn to read and recognise kanji characters, you should practise writing them. But rather than just copying them out endlessly, you need to use the power of active recall. He tells the student to use flashcards to test yourself on your ability to write the character from memory.
So for instance, on the front of the flashcard you have the word “man”, and then you recall the story ("oh yes, the POWER 力 in the RICE FIELD 田”) and write the kanji out from memory: 男.
The controversial part is the suggestion that you should do all of this work - make up 2000+ mnemonic stories, and learn to handwrite each kanji from memory - before learning how to read (i.e. pronounce) any of the kanji.
In practice, most students will be studying Japanese at the same time. (Who’s using the Heisig method to learn kanji, but not also learning the Japanese language? Nobody, I reckon.)
Combining the Heisig method with Anki
Heisig’s book was first published in 1977, so he suggests using paper flashcards. But the method really comes into its own when you use it with a flashcard app. I’l talk about Anki here because it’s the app I used.
Anki is a flashcard app that uses the principle of spaced repetition to make practising with flashcards as efficient as possible. Put simply, spaced repetition means the app decides when you need to see a flashcard next, based on how recently you got it right.
I used Anki for years, both for vocabulary practice and for kanji writing practice. It’s actually the reason I got a smartphone, in 2011.
You can make your own flashcard decks (a “deck” is what Anki calls a set of cards) with Anki, or you can download decks that other people have made. I used a deck that someone else made, but I edited it a bit.
On the front of the each card, I had the Heisig keyword. In this case, Heisig’s keyword is “eat”. This is a good keyword, as the kanji 食 means “eating” or “foodstuff”, and 食べる (taberu) is a verb meaning “to eat”. So, the idea is that you see the word “eat” and have to remember how to write the kanji:
How this works in practice
I probably practised writing kanji like this every day for about 15 minutes, for about a year and a half in 2010-2011. Essentially, that’s how I learned to write Japanese.
And by learning the meanings of kanji, suddenly all those signs and labels all around me (I was living in Japan by this time) started to have meaning.
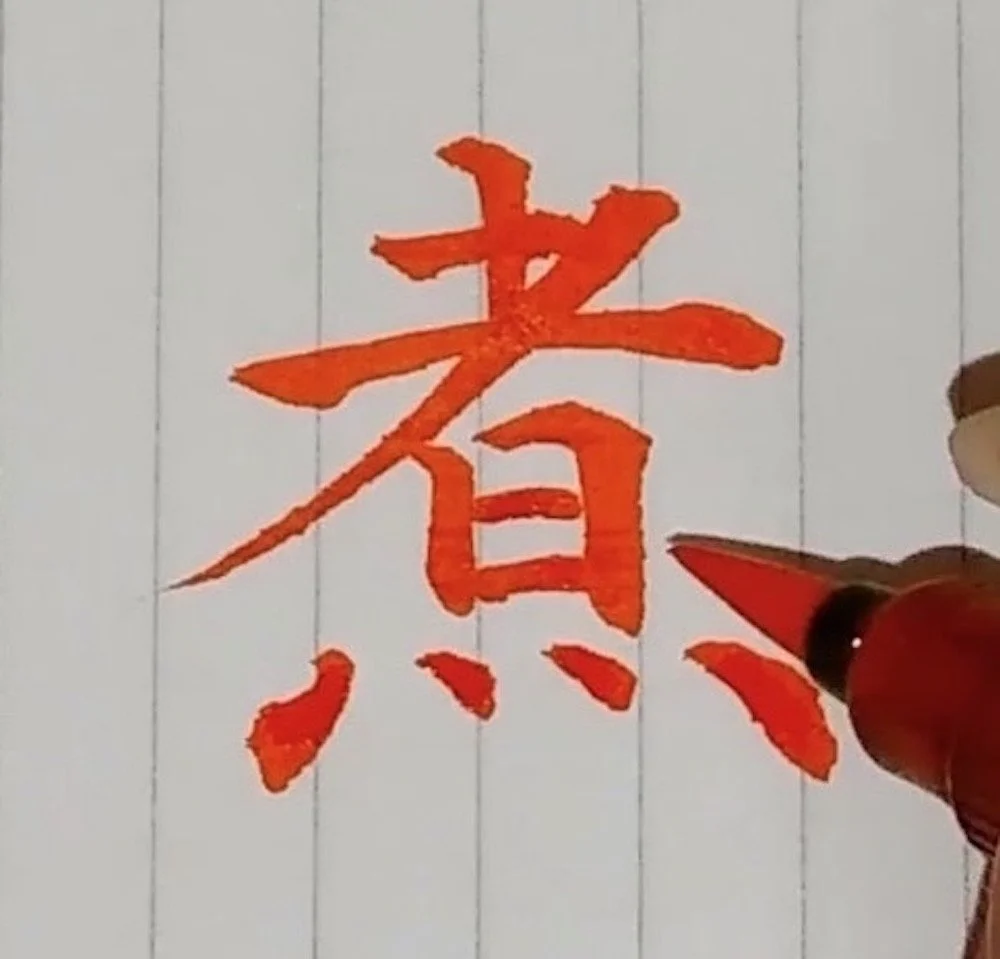
Outside my flat there was a sign with the word 歩行者 on it. I knew that 歩 meant “walk”, 行 meant “go”, and 者 meant “person”. That’s how I learned that 歩行者 means “pedestrian”. I didn’t know how to read it aloud, but I knew what it meant.
The school that I worked at was an eikaiwa gakkou, an English conversation school. On the front of the school was the word 英会話. I knew that 英 could mean “English”, 会 meant “meet”, and 話 meant “talk”. I also knew that the character 英 could be read as ei, because it was in the word 英語 (eigo, the English language). And that 話 could be read as wa, because it was at the end of 電話 (denwa, telephone). So from this I could guess that 英会話 was ei-something-wa… and I knew the word eikaiwa (English conversation), so I asked my boss if 英会話 was “eikaiwa” - yes.
I was vegetarian when I first moved to Japan, so I spent some time scouring packages in supermarkets to work out whether I could eat things or not. I knew that the radical 月 could mean “meat” or “flesh”, and I knew that 豕 meant “pig”, so I could guess that 豚 was probably “pork” or “pig”. I didn’t know the word for pig, or the word for pork. But I could guess that I probably didn’t want to eat something with 豚 in it.
In other words, the Heisig method works - when combined with other Japanese study.
(Incidentally, I don’t “teach” Heisig because it’s a bit weird, and not for everyone. But I don’t teach kanji through rote memorisation either. I use an integrated approach - I want students to learn the meaning of individual kanji, and the readings of whole words, and to learn kanji in context as much as possible. But I still think that Heisig is a great self-study method, and if you’re interested, you should check out his book*).
Post-Heisig
As my Japanese got better, I no longer associated the kanji with English keywords. When I saw the kanji 食 I’d think of the meaning - something to do with eating or food - but not necessarily Heisig’s keyword. So later, on the front of each card, I added an example word containing the kanji, which is written in hiragana. In this case, the word is たべる (taberu; to eat), and to test myself, I have to write out the word 食べる (i.e., not just the individual kanji):
I also have the stroke order on the back of the card, so that I can check straight away if the stroke order I wrote out is correct or not. I added these by screenshotting the stroke order diagram in takoboto, the dictionary app I use on my phone.
(I used to be a bit lazy about stroke order, but since I started teaching Japanese I have spent some time correcting my bad habits).
The stroke order diagram is good for checking that you’re handwriting the kanji in the correct way, too. A common mistake learners make is copying typeface fonts, but many kanji look quite different when handwritten to how they look in type.
In December 2019, I decided to dust off this (very neglected) Anki deck and do some handwriting practice, every day for a month. For twenty minutes every day, I’d go through flashcards and test myself on whether I could handwrite the kanji.
I really enjoyed the routine of practising kanji again. I find kanji practice surprisingly relaxing. I mentioned this to some students, and they (well some of them anyway!) said they find kanji writing practice relaxing, even meditative. Little and often is probably key.
Find something you enjoy, and do it every day forever
Years later, I was out for dinner with an American friend in Japan. We were looking at the kanji-filled handwritten menu, and I realised that his Japanese reading was really quick - much faster than mine. “How did you learn to read kanji?” I asked him.
“Er, I dunno. Just, reading books I guess? For, like, years.”
It probably doesn’t matter too much how you study kanji. To be honest, I’m not sure that the Heisig method is better than any other. It worked for me, but if you put the time in, there are other methods of learning kanji that might work just as well.
The key thing is to find something that works for you, and spend a little time on it every day. And if your friends laugh at you, try and ignore them! One day they might be asking you how you did it.
Related posts
Links
Links with an asterisk* are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission, at no extra cost to you, when you click through and buy the book. Thanks for your support!


































Like many people in the UK, I studied French in school. I liked French. I thought it was really fun to speak another language, to talk with people, and to try and listen to what was going on in a new country. (Still do!)
When I was 14 we went on a school exchange to the city of Reims, in northeastern France. I was paired with a boy, which I’m sure some 14-year-olds would find very exciting but which I found unbearably awkward. He was very sweet and we completely ignored each other.
That was nearly 20 years ago, and I didn’t learn or use any more French until, at some point in lockdown, I decided on a whim to take some one-to-one lessons with online teachers. Here are some things I learned about French, about language learning, and about myself.